Sometimes you need some fast machines and a lot of IOPS. SSD is the way to go there but what if your site is in Azure ?
Well build a high performance Storage space is Azure. Remember this setup will cost you some money or burn your MSDN credits is just one run.
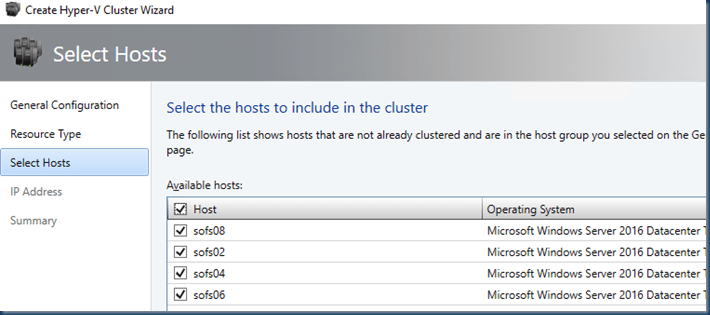
My setup is using several storage account and a setup of a 5 node cluster with a cloud witness and each node has 16 disk.

As the setup is based on Storage spaces direct I build a 5 node cluster. Some options are not needed but for my demo I need them in case you thought he why did he install this or that.
So building the Cluster
get-WindowsFeature Failover-Clustering
install-WindowsFeature "Failover-Clustering","RSAT-Clustering","File-Services", "Failover-Clustering","RSAT-Clustering -IncludeAllSubFeature –ComputerName "rsmowanode01.AZUTFS.local"
I add the other nodes later.
#Create cluster validation report
Test-Cluster -Node "rsmowanode01.AZUTFS.local “
New-Cluster -Name Owadays01 -Node "rsmowanode01.AZUTFS.local" -NoStorage -StaticAddress "10.0.0.20"
Now that my cluster is ready I added some disk to the VM’s and place them in several storage accounts. ( you can expand the default just make a Azure helpdesk request )
I have currently  not all needed but you will never know.
not all needed but you will never know.
 As I prep all my Azure VM’s in PowerShell here is an example on how to add the disk to the azure VM. As I need 16 disk for 5 nodes that are 80 disk with a 500 GB size 40 TB raw disks.
As I prep all my Azure VM’s in PowerShell here is an example on how to add the disk to the azure VM. As I need 16 disk for 5 nodes that are 80 disk with a 500 GB size 40 TB raw disks.
The powershell Sample command to create the disks.
Get-AzureVM -Name $vmname -ServiceName $vmname |
Add-AzureDataDisk -CreateNew -DiskSizeInGB 500 -DiskLabel ‘datadisk0’ -LUN 0 -HostCaching None |
Update-AzureVM
Now that the Cluster is ready and the disk are mounted to the Azure VM’s it is time for some magic
With the : Get-Disk | Where FriendlyName -eq ‘Msft Virtual Disk’|Initialize-Disk -PartitionStyle GPT -PassThru
all disk are online I do not need to format them as the disk are getting pooled

As every node gets his own storage enclosure
To enable the Storage space direct option you will need this to enable
(Get-Cluster).S2DEnabled
what you just did is making the local disk turn in to usable cluster disk.

to create a basic Storage pool
New-StoragePool -StorageSubSystemName Owadays01.AZUTFS.local -FriendlyName OwadaysSP01 -WriteCacheSizeDefault 0 -FaultDomainAwarenessDefault StorageScaleUnit -ProvisioningTypeDefault Fixed -ResiliencySettingNameDefault Mirror -PhysicalDisk (Get-StorageSubSystem -friendlyname "Clustered Windows Storage on Owadays01" | Get-PhysicalDisk)

|Initialize-Disk -PartitionStyle GPT -PassThru |New-Partition -AssignDriveLetter -UseMaximumSize |Format-Volume -FileSystem NTFS -NewFileSystemLabel "IODisk" -AllocationUnitSize 65536 -Confirm:$false

#Query the number of disk devices available for the storage pool
(Get-StorageSubSystem -Name Owadays01.AZUTFS.local | Get-PhysicalDisk).Count

Mirror storage spaces
Mirroring refers to creating two or more copies of data and storing them in separate places, so that if one copy gets lost the other is still available. Mirror spaces use this concept to become resilient to one or two disk failures, depending on the configuration.
Take, for example, a two-column two-way mirror space. Mirror spaces add a layer of data copies below the stripe, which means that one column, two-way mirror space duplicates each individual column’s data onto two disks.
Assume 512 KB of data are written to the storage space. For the first stripe of data in this example (A1), Storage Spaces writes 256 KB of data to the first column, which is written in duplicate to the first two disks. For the second stripe of data (A2), Storage Spaces writes 256 KB of data to the second column, which is written in duplicate to the next two disks. The column-to-disk correlation of a two-way mirror is 1:2; for a three-way mirror, the correlation is 1:3.
Reads on mirror spaces are very fast, since the mirror not only benefits from the stripe, but also from having 2 copies of data. The requested data can be read from either set of disks. If disks 1 and 3 are busy servicing another request, the needed data can be read from disks 2 and 4.

Mirrors, while being fast on reads and resilient to a single disk failure (in a two-way mirror), have to complete two write operations for every bit of data that is written. One write occurs for the original data and a second to the other side of the mirror (disk 2 and 4 in the above example). In other words, a two-way mirror requires 2 TB of physical storage for 1 TB of usable capacity, since two data copies are stored. In a three-way mirror, two copies of the original data are kept, thus making the storage space resilient to two disk failures, but only yielding one third of the total physical capacity as useable storage capacity. If a disk fails, the storage space remains online but with reduced or eliminated resiliency. If a new physical disk is added or a hot-spare is present, the mirror regenerates its resiliency.
Note: Your storage account is limited to a total request rate of up to 20,000 IOPs. You can add up to 100 storage accounts to your Azure subscription. A storage account design that is very application- or workload-centric is highly recommended. In other words, as a best practice, you probably don’t want to mix a large number of data disks for storage-intensive applications within the same storage account. Note that the performance profile for a single data disk is 500 IOPs. Consider this when designing your overall storage layout.
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/documentation/articles/azure-subscription-service-limits/#storage-limits

Now that the storage pools are in place we can do some measurements on the Speed creating disk and iops. based on Refs and NTFS
these disk I’m using for the Scale out file server
New-Volume -StoragePoolFriendlyName OWASP1 -FriendlyName OWADiskREFS14 -PhysicalDiskRedundancy 1 -FileSystem CSVFS_REFS –Size 2000GB

New-Volume -StoragePoolFriendlyName OWASP1 -FriendlyName OWADiskNTFS15 -PhysicalDiskRedundancy 1 -FileSystem NTFS –Size 20GB


With some disk changes and creation you can say the REFS with clustered shared volume is about 100x as fast!
Now that we have Cluster Storage I’m using this for the SOFS.
#create the SOFS
New-StorageFileServer -StorageSubSystemName Tech-SOFS.AZUTFS.local -FriendlyName Tech-SOFS -HostName Tech-SOFS -Protocols SMB

Adding the disk and the next test is ready.
First we make a couple a disk on the REFS share


so a 1TB disk creation is not much slower than a 100GB file remember these are fixed files.
When I do this on the NTFS volume and create a 100GB fixed disk this took forever after 10 Min I stopped the command. this is why you always do a quick format on a ntfs disk.

A 1Gb disk creation is a better test as you can see this is around 8 times slower with a 1000x smaller disk.

Let test IOPS for this I use the DISKSPD tool : Diskspd Utility: A Robust Storage Testing Tool (superseding SQLIO)
https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/DiskSpd-a-robust-storage-6cd2f223
So the disk creation is way way faster and when using this in a Hyper-v deployment the VM creation is way way faster en also the copy of files.


I did only READ test ! If you want also the Write test use –w1 the –b is the block size
Testing on REFS
C:\run\diskspd.exe -c10G -d100 -r -w0 -t8 -o8 -b64K -h -L \\tech-sofs\Tech-REFS01\testfil1e.dat
C:\run\diskspd.exe -c10G -d10 -r -w0 -t8 -o8 -b1024K -h -L \\tech-sofs\Tech-REFS01\testfil1e.dat

When using a little 10 sec burst we got high rates but this is not the goal.
C:\run\diskspd.exe -c10G -d10 -r -w0 -t8 -o8 -b1024K -h -L \\tech-sofs\Tech-REFS01\testfil1e.dat

Testing On NTFS
C:\run\diskspd.exe -c10G -d100 -r -w0 -t8 -o8 -b64K -h -L \\tech-sofs\Tech-NTFS01\testfil1e.dat


So basically you get much more IOPS then on a normal single disk but it all depends on block size configuration and storage usage normal or premium.
The main thing is if you want fast iops and machines it can be done in Azure it Will cost you but it is also expensive on premise.
C:\run\diskspd.exe -c10G -d100 -r -w0 -t8 -o8 -b4K -h -L \\tech-sofs\Tech-REFS01\testfil1e.dat
and with several runs you can get some nice results

but the the config I used is around the $30. total per hour
A8 and A9 virtual machines feature Intel® Xeon® E5 processors. Adds a 32 Gbit/s InfiniBand network with remote direct memory access (RDMA) technology. Ideal for Message Passing Interface (MPI) applications, high-performance clusters, modeling and simulations, video encoding, and other compute or network intensive scenarios.
A8-A11 sizes are faster than D-series
https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/pricing/details/virtual-machines/
Greetings,
Robert Smit
Cloud and Datacenter MVP ( Expertise: High Available )