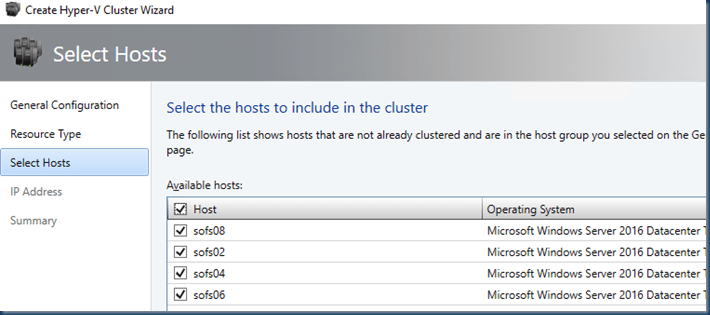
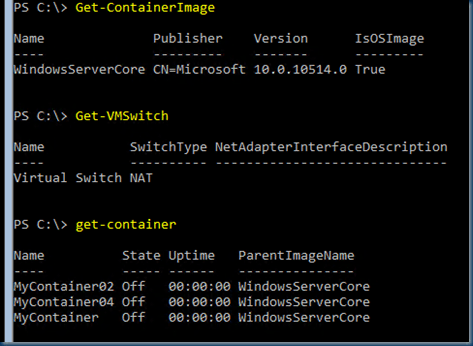
How ever Windows Server 2016 is supporting Rolling Upgrades Upgrading to Windows Server 2016 but this is only for a Cluster.
For other Servers you can upgrade your server or better reinstall. Bet you all choose for the Clean install.
Installation is the basic concept of getting the new operating system on your hardware. Specifically, a clean installation requires deleting the previous operating system. For information about installing Windows Server 2016, see System Requirements and Installation Information for Windows Server 2016. For information about installing other versions of Windows Server, see Windows Server Installation and Upgrade.
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server-docs/get-started/supported-upgrade-paths
Well in this case I try a sample Domain controller. This has several roles and is migrated from 2008<>2012<>2012R2 and now to 2016 so is this the best option ? Well this DC has ADFS,CA,had Identity Management for UNIX. So a not so typical DC.
So I removed all unneeded components like ADFS and the Identity Management for UNIX was not available on my DC. ( did not make a screenshot )
no mater what I did I need to deinstall the components the following article was a help https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731178(v=ws.11).aspx
Well not totally the message was still there reboot / showdown nothing. Was there anything stuck on this DC ?
Well this the DC is getting replaced the fastest way Clean install. I build a new DC with Windows Server 2016 installed the AD role on the server. Important is moving the FSMO roles.
After I did a Forest prep and Domain prep I joined the Server to the domain.
Finding the FSMO roles
netdom query fsmo
Moving the Roles can done in the old way but also in powershell
Move-ADDirectoryServerOperationMasterRole -Identity “Your-DC” -OperationMasterRole SchemaMaster,RIDMaster,InfrastructureMaster,DomainNamingMaster,PDCEmulator
After I moved the FSMO roles and rebooted and Updated both DC’s I thought lets find why the upgrade won’t work on the original Domain controller.
After I started the upgrade I was shocked that the Upgrade had no Issues anymore. Leasons learned In case of Upgrading the Domain controller and you have some Issues : create a new DC and Join move the FSMO roles reboot the DC’s and try again if you really need this DC. but a Clean OS install is much faster and better but you will need to install some apps again or tools. maybe this is a good time to automate this.
Installing or removing Identity Management for UNIX by using a command line
Quick reference table of supported upgrade paths from older Windows Server retail editions to Windows Server 2016 retail editions:
| If you are running these versions and editions: | You can upgrade to these versions and editions: |
| Windows Server 2012 Standard | Windows Server 2016 Standard or Datacenter |
| Windows Server 2012 Datacenter | Windows Server 2016 Datacenter |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard | Windows Server 2016 Standard or Datacenter |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter | Windows Server 2016 Datacenter |
| Hyper-V Server 2012 R2 | Hyper-V Server 2016 (using Cluster OS Rolling Upgrade feature) |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 Essentials | Windows Server 2016 Essentials |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Standard | Windows Storage Server 2016 Standard |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 Workgroup | Windows Storage Server 2016 Workgroup |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 R2 Standard | Windows Storage Server 2016 Standard |
| Windows Storage Server 2012 R2 Workgroup | Windows Storage Server 2016 Workgroup |
License conversion
You can convert Windows Server 2016 Standard (retail) to Windows Server 2016 Datacenter (retail).
You can convert Windows Server 2016 Essentials (retail) to Windows Server 2016 Standard (retail).
You can convert the evaluation version of Windows Server 2016 Standard to either Windows Server 2016 Standard (retail) or Datacenter (retail).
You can convert the evaluation version of Windows Server 2016 Datacenter to Windows Server 2016 Datacenter (retail).
Upgrading to Windows Server 2012 R2
For details, including important caveats and limitations on upgrade, license conversion between editions of Windows Server 2012 R2, and conversion of evaluation editions to retail, see Upgrade Options for Windows Server 2012 R2.
Quick reference table of supported upgrade paths from older Windows Server retail editions to Windows Server 2012 R2 retail editions:
| If you are running: | You can upgrade to these editions: |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Datacenter with SP1 | Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Enterprise with SP1 | Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard or Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter |
| Windows Server 2008 R2 Standard with SP1 | Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard or Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter |
| Windows Web Server 2008 R2 with SP1 | Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard |
| Windows Server 2012 Datacenter | Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter |
| Windows Server 2012 Standard | Windows Server 2012 R2 Standard or Windows Server 2012 R2 Datacenter |
| Hyper-V Server 2012 | Hyper-V Server 2012 R2 |
License conversion
You can convert Windows Server 2012 Standard (retail) to Windows Server 2012 Datacenter (retail).
You can convert Windows Server 2012 Essentials (retail) to Windows Server 2012 Standard (retail).
You can convert the evaluation version of Windows Server 2012 Standard to either Windows Server 2012 Standard (retail) or Datacenter (retail).
Use Full Links :
Upgrade and conversion options for Windows Server 2016 https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server-docs/get-started/supported-upgrade-paths
Release Notes: Important Issues in Windows Server 2016 https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server-docs/get-started/windows-server-2016-ga-release-notes
What’s New in Windows Server 2016 https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server-docs/get-started/what-s-new-in-windows-server-2016-technical-preview-5
Server role upgrade and migration matrix for Windows Server 2016 https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server-docs/get-started/server-role-upgradeability-table?f=255&MSPPError=-2147217396
Cluster operating system rolling upgrade https://technet.microsoft.com/windows-server-docs/failover-clustering/cluster-operating-system-rolling-upgrade
Follow Me on Twitter @ClusterMVP
Follow My blog https://robertsmit.wordpress.com
Linkedin Profile Http://nl.linkedin.com/in/robertsmit
Google Me : https://www.google.nl
Bing Me : http://tinyurl.com/j6ny39w